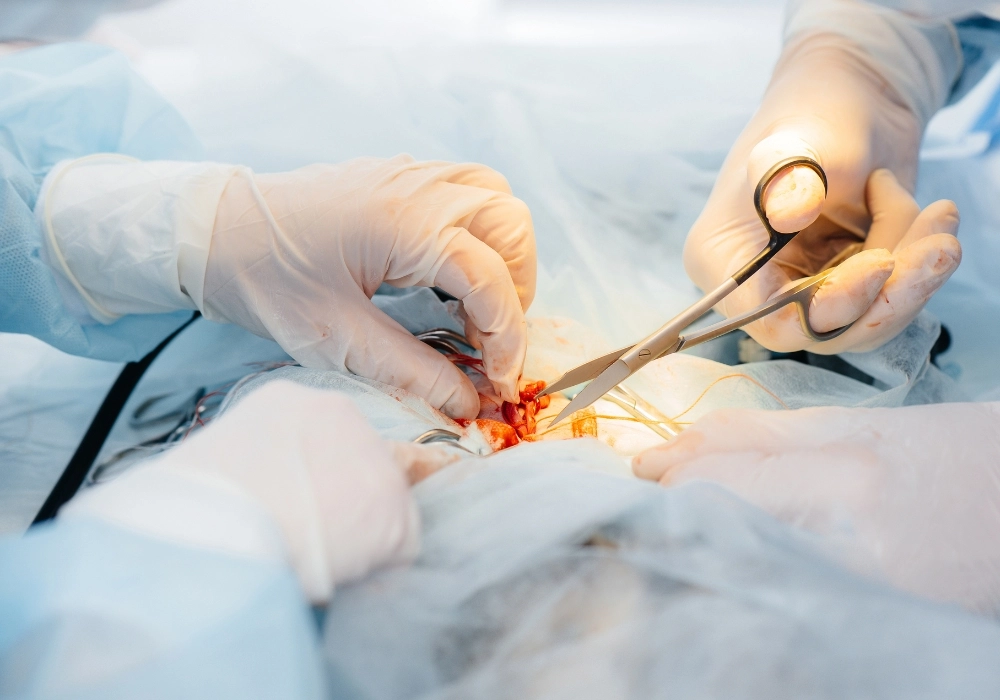
Varicocele repair is a surgical intervention used to correct varicoceles, which are abnormal enlargements of the veins within the scrotum. Varicoceles are similar to varicose veins and often develop due to malfunctioning valves in the veins, causing blood to pool and the veins to dilate. While many men with varicoceles experience no symptoms, some develop complications such as testicular pain, infertility, or testicular atrophy, all of which can be alleviated through varicocele repair.
Varicoceles primarily occur on the left side of the scrotum and are most common in men between the ages of 15 and 35. Approximately 10 to 15 percent of all men have varicoceles, but not all of them require treatment. Varicocele repair is recommended for men experiencing persistent discomfort, fertility issues, or testicular damage caused by the condition. Early detection and intervention can help prevent long-term complications.
The goal of varicocele repair is to improve blood flow by closing off the enlarged veins and rerouting blood through healthier veins. The procedure can significantly improve testicular function and sperm quality, offering an effective treatment for men who suffer from varicocele-related infertility.
There are different types of varicocele repair, including open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, and percutaneous embolization. Each method has its benefits, depending on the patient’s specific condition. Open surgery is the most common, but laparoscopic and embolization techniques are increasingly popular due to their minimally invasive nature and quicker recovery times.
Causes and Symptoms of Varicocele
Varicoceles occur when the valves inside the veins in the scrotum fail to work properly, leading to blood pooling and vein enlargement. While the exact cause of this valve malfunction is unknown, it is believed to be related to the anatomy of the testicular veins and their drainage patterns.
Common symptoms that may prompt the need for varicocele repair include:
- A dull ache or discomfort in the scrotum, especially after standing or physical activity
- A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- Visible or palpable enlarged veins in the scrotum, often described as a “bag of worms”
- Testicular atrophy or shrinkage
- Fertility problems, including reduced sperm count and quality
By understanding these symptoms and the potential long-term consequences of untreated varicoceles, men can seek early medical advice and determine whether varicocele repair is necessary.
When it comes to varicocele repair, there are several surgical techniques available, each offering specific benefits and varying recovery times. The right choice of surgery depends on the patient’s condition, the severity of the varicocele, and personal preferences regarding recovery.
- Open Surgery (Microsurgical Varicocelectomy)
Microsurgical varicocelectomy is the most traditional form of varicocele repair. In this procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the lower abdomen or groin to access the affected veins. A surgical microscope is often used to enhance precision during the procedure. The dilated veins are identified, and the surgeon carefully ties them off, preventing blood from pooling in the scrotum.
Microsurgical varicocelectomy is highly effective, with a low risk of complications or recurrence. It is the preferred method for men experiencing infertility due to varicoceles, as it offers a high success rate in improving sperm quality. Recovery from open surgery typically takes a few weeks, and men can resume normal activities within two weeks.
- Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive alternative to open surgery. During this procedure, the surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a camera (laparoscope) and surgical instruments to access the varicocele. The enlarged veins are tied off, much like in open surgery.
Laparoscopic varicocele repair offers the advantage of smaller incisions, reduced pain, and faster recovery times compared to open surgery. However, it requires general anesthesia and is more expensive than traditional surgery. Most patients can return to their normal activities within a week, with full recovery expected within 4-6 weeks.
- Percutaneous Embolization
Percutaneous embolization is a non-surgical, minimally invasive procedure for varicocele repair. A radiologist inserts a catheter through a small incision in the groin or neck and uses imaging guidance to position it near the affected veins. A coil or solution is then injected to block the veins, preventing blood from pooling in the scrotum. Over time, the body naturally reroutes blood through healthier veins.
Embolization is an outpatient procedure that requires less recovery time than traditional surgery. It is ideal for patients who want to avoid a surgical approach, though it may not be as effective for larger varicoceles. Recovery typically takes a few days, and patients can resume their regular activities within a week.
Each method of varicocele repair has its advantages and potential risks, and the choice of procedure should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the best option based on the patient’s unique circumstances.
Varicocele repair is not always necessary, but it becomes an essential treatment option when certain conditions are present. Understanding the indications for surgery helps patients decide when it’s time to seek medical intervention.
- Persistent Pain and Discomfort
One of the most common reasons for seeking varicocele repair is pain and discomfort in the scrotum. While some varicoceles are asymptomatic, others can cause a dull ache or heaviness, especially after prolonged standing, physical exertion, or during sexual activity. Pain can range from mild to severe, affecting daily life and activities. Surgery is often recommended when the pain persists despite conservative treatments like rest or pain relief medications.
- Infertility
Varicoceles are a known cause of male infertility, affecting sperm production and quality. The abnormal veins can raise the temperature in the scrotum, leading to reduced sperm count, motility, and abnormal sperm morphology. For men experiencing infertility, varicocele repair can improve sperm parameters and increase the chances of natural conception or success with assisted reproductive techniques like IVF (in vitro fertilization).
- Testicular Atrophy
Testicular atrophy, or the shrinkage of the testicles, can occur due to long-standing varicoceles. This condition is a result of impaired blood flow and increased pressure in the veins, which can damage the testicular tissue over time. Varicocele repair can prevent further atrophy and may help restore some testicular function. Early intervention is crucial in preserving fertility and testicular health.
- Declining Testicular Function
Men who experience declining testicular function, as indicated by abnormal semen analysis or hormone levels, may benefit from varicocele repair. Surgical intervention can halt the progression of the condition and improve sperm production. While not all men with varicoceles experience fertility issues, those who do often see marked improvements following surgery.
Conservative Management vs. Surgery
Not all varicoceles require surgery, especially in cases where there are no symptoms, and fertility is not a concern. In such cases, conservative management may include regular monitoring, pain management, and lifestyle modifications. However, for men experiencing pain, fertility issues, or testicular atrophy, varicocele repair is the best option for preventing further complications and restoring testicular health.
Recovery after varicocele repair depends on the type of surgery performed and the patient’s overall health. While the recovery process is generally quick and uncomplicated, patients must adhere to specific guidelines to ensure a smooth recovery and prevent complications.
- Post-Surgical Care
Immediately after surgery, patients may experience mild pain, swelling, and bruising around the incision site or scrotum. These symptoms are normal and usually resolve within a few days. Pain can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications or prescribed painkillers, and patients are advised to apply ice packs to the affected area to reduce swelling.
Keeping the surgical site clean and dry is essential to prevent infection. Patients should avoid soaking in baths or swimming pools for at least two weeks after surgery. Instead, they should opt for quick showers and pat the area dry afterward.
- Activity Restrictions
During the first week after varicocele repair, patients should rest and avoid strenuous physical activities, including heavy lifting, running, and sexual activity. Light walking is encouraged to improve blood circulation and promote healing. Patients should gradually increase their activity levels as they begin to feel better, but they must follow their surgeon’s guidelines on when it is safe to resume more vigorous activities.
- Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are essential to ensure that the surgical site is healing properly and that there are no complications, such as infections or recurrence of the varicocele. The surgeon will assess the patient’s progress and provide further recommendations on activity restrictions and when to resume normal activities.
- Return to Work and Normal Activities
Most men can return to work within a week, especially if their job does not involve heavy physical labor. Those with physically demanding jobs may need to take additional time off to ensure full recovery. Full recovery from varicocele repair typically takes 4-6 weeks, during which time the body continues to heal, and the veins adjust to the new blood flow patterns.
For men undergoing varicocele repair for infertility, improvements in sperm quality may take 3-6 months, as sperm production takes time to normalize. Follow-up semen analysis is usually recommended to evaluate the success of the surgery in improving fertility.
The cost of varicocele repair can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the type of surgery performed, the surgeon’s experience, the healthcare facility, and geographic location. Understanding these cost factors can help patients plan for the financial aspects of the procedure and explore available options for coverage.
- Surgical Method
The type of varicocele repair surgery chosen—whether open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or embolization—has a significant impact on the overall cost. Open surgery is typically less expensive than laparoscopic or embolization procedures, but the latter two methods often offer quicker recovery times, which may appeal to some patients despite the higher costs.
- Surgeon’s Expertise
The surgeon’s experience and specialization in urology or fertility surgery can also influence the cost. Surgeons with advanced training or expertise in microsurgical techniques may charge more for their services, but the success rates and reduced complication risks often justify the additional cost.
- Healthcare Facility
The cost of varicocele repair is also influenced by the facility where the procedure is performed. Hospitals generally have higher fees than outpatient surgery centers or private clinics. Additionally, hospitals in major cities may charge more than those in smaller towns or rural areas.
- Insurance Coverage
Many health insurance plans cover varicocele repair if the procedure is deemed medically necessary. This includes cases where the patient experiences pain, testicular atrophy, or infertility. Patients should contact their insurance provider to confirm coverage and inquire about any potential out-of-pocket costs, such as co-pays, deductibles, or pre-authorization requirements.
In cases where varicocele repair is not covered by insurance, patients may explore financing options or payment plans offered by the healthcare facility. Understanding the full cost of the procedure beforehand allows patients to make informed financial decisions.